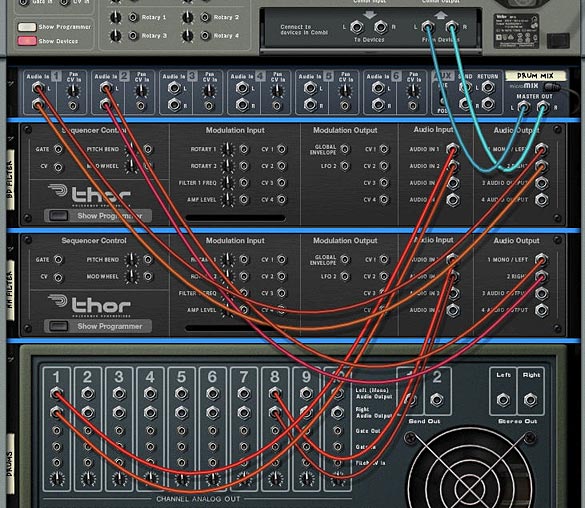
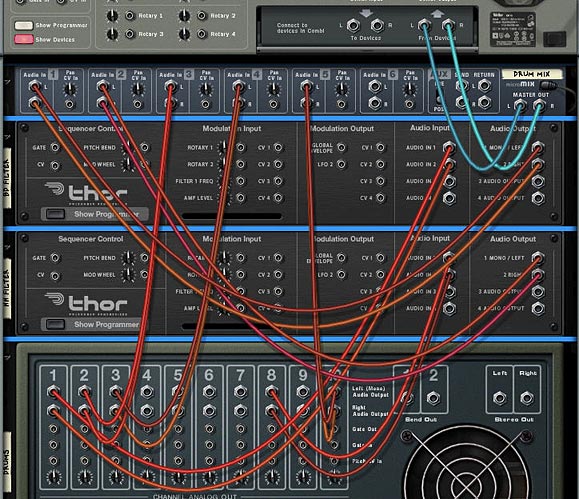
In this tutorial I’m going to show you how to create a flexible FX chain that has 8 stops along the chain, and at each of these stops, allows you to select from 1 of 6 different FX devices. This means you have a total of 48 different FX devices to select from in the chain, and the possible permutations of all these FX are 8×7 possible FX combinations, which amounts to 40,320 possible FX chain permutations. Don’t believe me? Go here: http://www.vpgenius.com/tools/combin.aspx. That’s a hell of a lot of possibilities. Now change the order of your FX chains, and you end up with double, triple and even more possibilities. So let’s see how it’s all done.
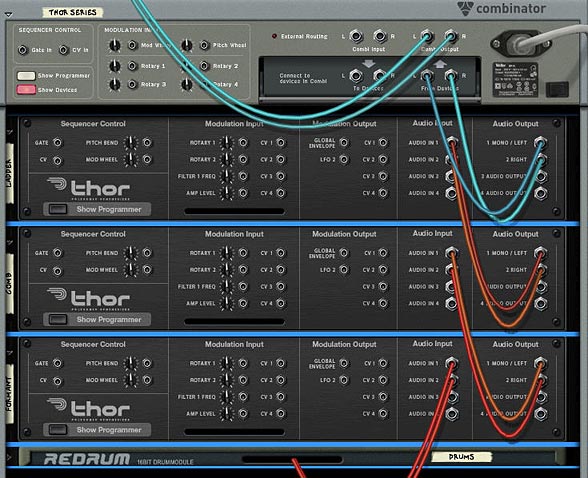
You can download the project files here: Kong-FX-Chain-Builders. The file contains 3 different FX chain combinators that are outlined below. The effects in each chain are the same. The only difference is that they each present the chain in a different order. You can take this idea and build any number of effects chains in any order you wish to combine both “Serial” and “Parallel” processing of your audio signal through various FX that you create in Reason. It’s all only limited by your own imagination.
Introducing the “Kong FX Chain Builder” Patch
The beauty of this type of system lies also in the fact that you can combine a “Serial” and “Parallel” audio system together. So when I was working on my “Key Flux FX Processor” in project number 56 here on my site, I introduced the notion of a Parallel system, whereby the same audio was sent through many different FX chains and then sent out to the soundcard. In this tutorial, I’m going to introduce the idea of a Serial FX system, and merge it with a Parallel FX system so that you get much more flexible audio routing and audio possibilities.
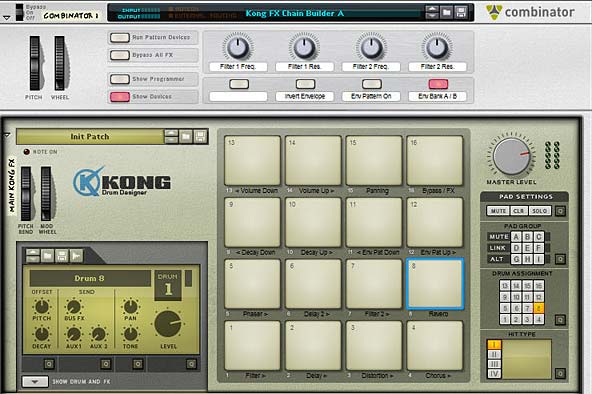
The idea is pretty simple. First you have a set of FX in a chain, as follows:
Filter > Delay > Distortion > Chorus > Phaser > Delay 2 > Filter 2 > Reverb
Now, each of these “stops” along the chain also has 7 different selectable FX sound possibilities, as follows:
| Filter>
(Pad 1) |
Delay>
(Pad 2) |
Distortion>
(Pad 3) |
Chorus>
(Pad 4) |
Phaser>
(Pad 5) |
Delay2>
(Pad 6) |
Filter2>
(Pad 7) |
Reverb>
(Pad 8 ) |
| FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 |
| FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 |
| FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 |
| FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 |
| FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 |
| FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 |
| Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio |
The Dry audio is there so that you have a selection that sets things back to being the original audio, like a pass-through. Using this table you can come up with an amazingly large array of different sounds by mixing and matching the different FX together. You can, for instance, create the following:
| Filter >
(Pad 1) |
Delay >
(Pad 2) |
Distortion >
(Pad 3) |
Chorus >
(Pad 4) |
Phaser >
(Pad 5) |
Delay 2 >
(Pad 6) |
Filter 2 >
(Pad 7) |
Reverb >
(Pad 8 ) |
| FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 | FX 1 |
| FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 | FX 2 |
| FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 | FX 3 |
| FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 | FX 4 |
| FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 | FX 5 |
| FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 | FX 6 |
| Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio | Dry Audio |
And that is just one example.
Switching the Order of Effects in the Chain
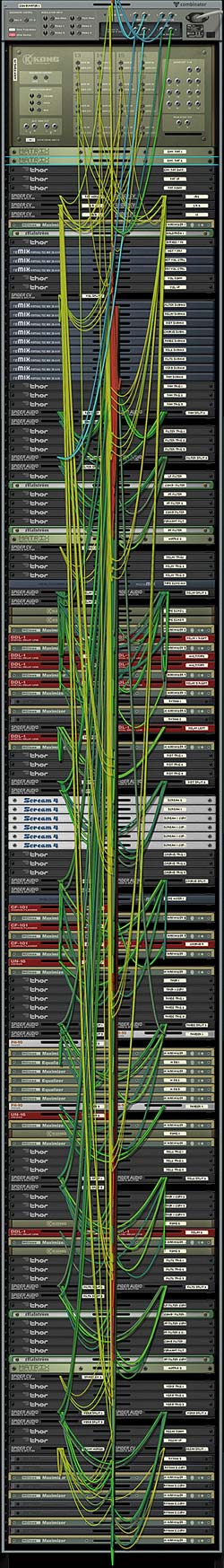
Now I know some of you are going to say, “well why can’t I switch the order of the FX chain?” So instead of having the Filter come before the Delay, how about switching it so that the Filter comes after the delay. And to that I’ll say that Reason is not the easiest software to work with when it comes to making routing decisions such as these and building it into a single setup is very difficult. But thankfully it’s pretty easy to build multiple instances of the Combinator to come up with any FX chain order you like. The trick is to flip to the back of the rack and change the following:
- The order of the “Gate Out” CVs from the first 8 Kong Pads
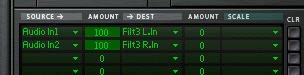
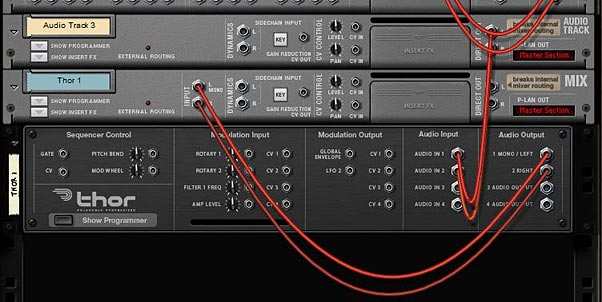
- The order of the 14:2 Submixers and their associated splitters. The signal flow goes from the “To Devices” of the Combinator into the first Effect’s splitter. Then the 14:2 Submix main output of the first effect goes into the second effect’s splitter. And so on down the chain, until the final output goes into the Pan splitter device. The Pan also has a bank of different “Global” LFO Panning selections. This can be selected on Pad 15.
So anyway, this just shows you that with a little thought, you can create a variety of FX of your own and route them in a serial way. Then use the “Parallel” processing idea to create multiple effects at each stop in the chain. Simple enough right?
Here are the other 2 effect chains I came up with. Feel free to create your own based on variations that work for you. You can either change the routing scheme as I outlined above, or you can change the actual effects at each stop. As you can see, you don’t even need to have all the FX in play within the chain. You can keep any part of the chain set to “Dry Audio” so that it will not be affecting the chain at all. This means you can make your chain simple with only 1 effect in play, all 8 in play, or any amount in between. Here are the other two effect chains I put together:
Delay > Filter > Phaser > Delay 2 > Chorus > Filter 2 > Reverb > Distortion
Phaser > Chorus > Filter > Reverb > Distortion > Delay > Delay 2 > Filter 2
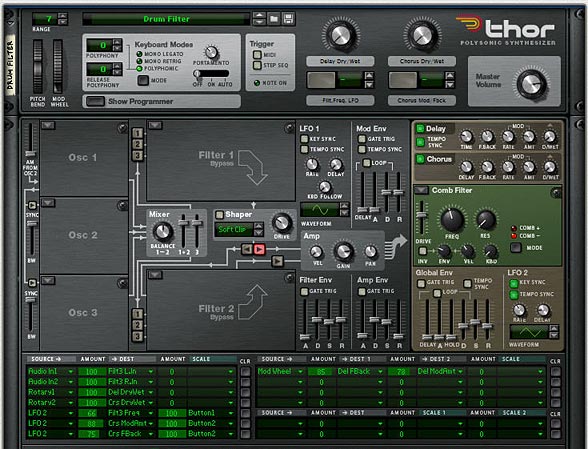
Working with the “Kong FX Chain Builder”
There are 2 components to working with the Kong FX Chain Builder: 1. The Combinator and 2. The Kong device. Both work together to create your FX chain. You can also use them “Live” and play the different effects out on the pads in real-time, or else build them up in the studio until you find a combination of effects that works for your sound, and then just leave this setting as it is (or save it for future recall).
I’ll start off with the Kong device. Note that if you want to fully utilize the device, you should create a track for it in Reason or Record’s Main Sequencer. This way, you can not only play the Kong device, but also record your Kong pad changes over time. And you can also lock your pad control surface to the Kong device and another controller to the Combinator; essentially controlling them both via 2 different controllers at the same time. So here are all the Kong pad settings:
- Pads 1 to 8: These are the 8 stops in the FX chain going from Pad 1 > 2 > 3 > 4 > 5 > 6 > 7 > 8. In the original file I created (Kong FX Chain Builder A), this goes from Filter > Delay > Distortion > Chorus > Phaser > Delay 2 > Filter 2 > Reverb. The Pads act as a cycle, starting with a dry signal, then going through 6 different possible FX. The pad cycles through these 7 positions. So each time the pad is pressed, you’ll hear a new effect inserted into the chain.
- Pads 9 and 10: Decay Down / Decay Up – These pads will shift the decay of all the Reverb effects upward or downward. So you need to have the Reverb effect turned on (in other words, you need to have one of the 6 Reverbs enabled; not the dry signal).
Note that there is an upper and lower limit, which, when reached, will not go any further. However, the pad can continue to go upward or downward for a few more times. This means that if you push the decay all the way to zero, and still hit the “Decay Down” pad, it will continue to move downward. So it may take a few more Pad pushes on the “Decay Up” pad to get it back to a “zero” postion (until you start hearing the decay again). This is true of all the Up/Down pads. - Pads 11 and 12: Envelope Pattern Down / Envelope Pattern Up – These pads will shift the matrix pattern banks upward or downward. These curve patterns are used to “play” the envelope amount on all the filters in the system. Therefore, you need to have at least one filter turned on to hear anything. You also need to have the “Env Pattern On” button (button 2 on the Combinator) enabled. There are 25 patterns on each Matrix (from A1 to D1), for a total of 50 patterns from which to select (you need to use Button 4 on the Combinator to switch between Matrix A and Matrix B).
Note that there is an upper and lower limit, which, when reached, will not go any further. However, the pad can continue to go upward or downward for a few more times. This means that if you push the patterns all the way down to A1 on the Matrix, and still hit the “Env Pat Down” pad, it will continue to move downward. So it may take a few more Pad pushes on the “Env Pat Up” pad to get it back to the “A1” postion (and get the patterns to start moving forward again). This is true of all the Up/Down pads. - Pads 13 and 14: Volume Down / Volume Up – These pads will shift the global volume upward or downward. Note that there is an upper and lower limit, which, when reached, will not go any further. However, the pad can continue to go upward or downward for a few more times. This means that if you push the volume all the way down to zero, and still hit the “Volume Down” pad, it will continue to move downward. So it may take a few more Pad pushes on the “Volume Up” pad to get it back to a “zero” postion (until you start hearing the volume again). This is true of all the Up/Down pads.
- Pad 15: Panning. You can select from 6 different Auto-panning effects, which are global and affect the signal after it has gone through all 8 effect stops in the chain. There is also a seventh “dry” position, which is on by default. The Pad cycles through all 7 positions (6 “auto-panners” and 1 “dry” position).
- Pad 16: FX / Bypass – this allows you to switch between hearing the effects chain or hearing the original “dry” signal.
The Combinator controls are outlined below:
- Pitch Bend: Not assigned.
- Mod Wheel: Controls the envelope amount on all the filters. This is used in conjunction with the Envelope patterns in both Matrixes that also control the envelope amount. In other words, you can use the Mod Wheel to scale the envelope amount, and therefore, how much the envelope is affected by the patterns or not. If you wish to control the envelope amount without having any patterns control the envelope, disable button 3 on the Combinator, and then use the Mod Wheel, which will now be the only parameter affecting the amount of envelope applied to the filter(s).
Note also that both the Mod Wheel and the Patterns affect all filter envelopes globally; both “Filter 1” and “Filter 2.” And of course, at least one filter needs to be added into the FX chain for you to hear the effect of the Mod Wheel or Patterns applied to the Filter Envelope amount. - Rotary 1: Filter 1 Frequency. Adjusts the Frequency of the first filter in the chain. All the filter selections for “Filter 1” are affected using this rotary, so that as long as you have one of the six filters enabled in the Filter 1 slot, the Frequency can be adjusted.
- Rotary 2: Filter 1 Resonance. Adjusts the Resonance of the first filter in the chain. All the filter selections for “Filter 1” are affected using this rotary, so that as long as you have one of the six filters enabled in the Filter 1 slot, the Resonance can be adjusted.
- Rotary 3: Filter 2 Frequency. Adjusts the Frequency of the second filter in the chain. All the filter selections for “Filter 2” are affected using this rotary, so that as long as you have one of the six filters enabled in the Filter 2 slot, the Frequency can be adjusted.
- Rotary 4: Filter 2 Resonance. Adjusts the Resonance of the second filter in the chain. All the filter selections for “Filter 2” are affected using this rotary, so that as long as you have one of the six filters enabled in the Filter 2 slot, the Resonance can be adjusted.
- Button 1: Not Assigned.
- Button 2: Invert Envelope. This is a simple envelope invert button, and affects all filters in both the “Filter 1” and “Filter 2” slots in the FX chain.
- Button 3: Envelope Pattern On. This turns on the envelope pattern Matrixes so that the curve pattern that is selected in Matrix A or B will affect the envelope amount of all Filters in both “Filter 1” and “Filter 2” slots in the FX chain. There are 2 parameters that both affect the Filter Envelope Amount: The pattern here, and the Mod Wheel. The higher you raise the Mod Wheel, the higher the Envelope amount. You can use a combination of the pattern and Mod Wheel to effectively “play” with the Filter Envelope Amount parameter. The reason I set it up this way is that you have ultimate control over the envelope amount. For example, you can turn off the pattern by keeping this button (button 3) disabled. Then use the Mod Wheel to scale the amount upward or leave it fully off (when the Mod Wheel is fully down). Or you can turn on the pattern and leave the mod wheel fully down to have the amount controlled solely by the pattern. Or use both in combination to play around with the envelope amount.
- Button 4: Envelope Bank A / B. Selects between the two pattern banks (2 Matrixes) that affect the Envelope Amount parameter on all filters (read above for more information). There are 25 patterns on each Matrix (from A1 to D1), for a total of 50 patterns from which to select. Button four switches between the first 25 patterns on Matrix A (when the button is disabled) to the second set of 25 patterns on Matrix B (when the button is enabled).
Visualizing the active FX Chain
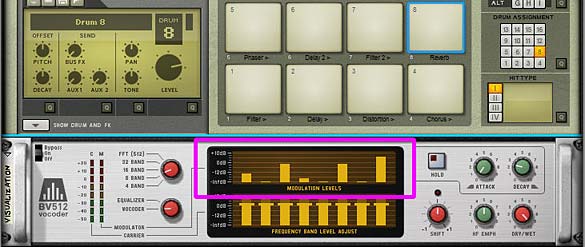
Sterioevo over at Mute.Hate.Loud.Love was kind enough to provide two methods for visualizing the active effect chain (see the comments below this post for more info about this CV method). He used the Gate Length of the Thor Trigger devices to change the Modulation Level Bands of the BV512 Vocoder and the delay steps in the DDL delay devices to show visually which effect was enabled at each stop in the FX chain. So I updated the patches (just download the Project files again if you haven’t already) using his “Vocoder Visualization” method. You’ll now see a Vocoder under the main Kong device. This uses an 8-band setting to display the position of each effect on Pads 1-8 in the Kong device. This way you can visualize what’s going on as you play the pads. Very cool and handy little tool! Thanks Steve!
So what do you think of this combination of “Parallel” and “Serial” effects processing using Kong? Any other ideas come to mind on how these ideas can be used? I can envision setting both this and the “Key Flux FX Processor” ideas on the alternate devices. For example, you could set up the “Key Flux FX Processor” on Kong and you can probably set up the “FX Chain Builder” on a Combinator. The device is somewhat irrelevant. What matters is the concepts and what you want to accomplish. And as you can see, Reason can usually provide an avenue to make your systems come to life.
Until next time, hope you can make this work for you and use it in your own productions. If you do, drop me a line and let me see what you come up with. I’m always interested to see how others’ use my patches. Cheers for now.